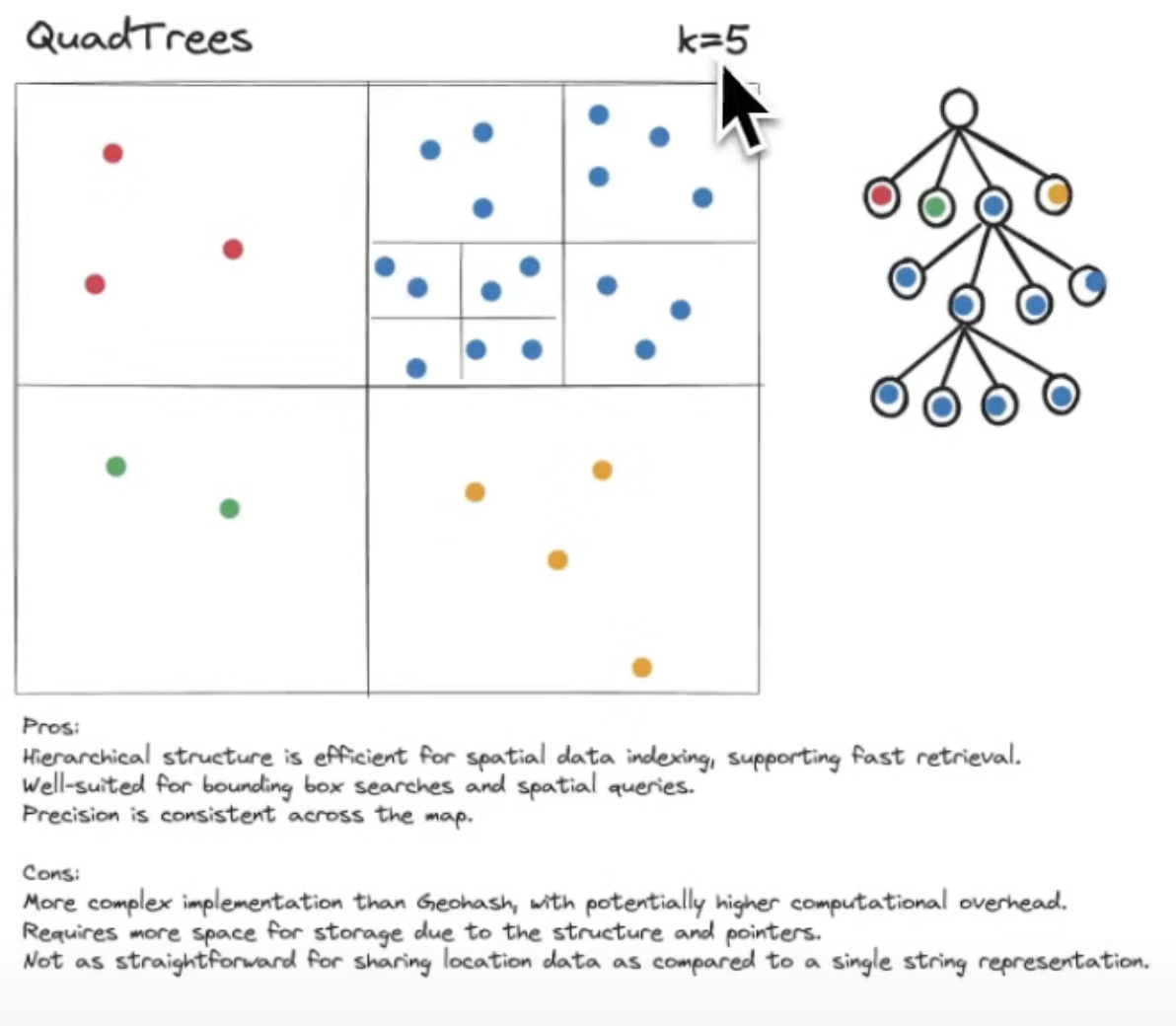
A quadtree is a tree data structure that recursively subdivides a two‑dimensional space into four quadrants or regions. It’s commonly used for:
- Spatial indexing (e.g. storing points, polygons, images)
- Collision detection in games
- Image compression (subdivide until uniform color)
Basically the way it works is storing 2D data in two-dimensional space. And when a certain two-dimensional space gets to packed it subdivides that space into smaller 2D spaces. It can do this via trees.
from typing import List, Tuple
Point = Tuple[float, float]
class Rectangle:
def __init__(self, x: float, y: float, hw: float, hh: float):
self.x, self.y, self.hw, self.hh = x, y, hw, hh
def contains(self, p: Point) -> bool:
px, py = p
return (self.x - self.hw <= px <= self.x + self.hw and
self.y - self.hh <= py <= self.y + self.hh)
def intersects(self, other: "Rectangle") -> bool:
# Axis‐aligned center‐distance check
dx = abs(self.x - other.x)
dy = abs(self.y - other.y)
return (dx <= self.hw + other.hw) and (dy <= self.hh + other.hh)
class QuadTree:
def __init__(self, boundary: Rectangle, capacity: int = 4):
self.boundary = boundary # this node’s region
self.capacity = capacity # max before subdividing
self.points: List[Point] = [] # only used if leaf
self.divided = False
def subdivide(self):
x, y, hw, hh = self.boundary.x, self.boundary.y, self.boundary.hw, self.boundary.hh
ne = Rectangle(x + hw/2, y - hh/2, hw/2, hh/2)
nw = Rectangle(x - hw/2, y - hh/2, hw/2, hh/2)
sw = Rectangle(x - hw/2, y + hh/2, hw/2, hh/2)
se = Rectangle(x + hw/2, y + hh/2, hw/2, hh/2)
self.northeast = QuadTree(ne, self.capacity)
self.northwest = QuadTree(nw, self.capacity)
self.southwest = QuadTree(sw, self.capacity)
self.southeast = QuadTree(se, self.capacity)
# Reallocate existing points into the appropriate children
for p in self.points:
(self.northeast.insert(p) or
self.northwest.insert(p) or
self.southwest.insert(p) or
self.southeast.insert(p))
self.points.clear()
self.divided = True
def insert(self, p: Point) -> bool:
# 1) Reject if outside this region
if not self.boundary.contains(p):
return False
# 2) If we're a leaf, try to store or subdivide
if not self.divided:
if len(self.points) < self.capacity:
self.points.append(p)
return True
# capacity reached ⇒ split and reallocate
self.subdivide()
# 3) Delegate to whichever child contains p
return (
self.northeast.insert(p) or
self.northwest.insert(p) or
self.southwest.insert(p) or
self.southeast.insert(p)
)
def query(self, range_rect: Rectangle, found: List[Point] = None) -> List[Point]:
if found is None:
found = []
# If no overlap, skip entirely
if not self.boundary.intersects(range_rect):
return found
# If leaf, check local points
if not self.divided:
for p in self.points:
if range_rect.contains(p):
found.append(p)
else:
# Otherwise recurse into children
self.northwest.query(range_rect, found)
self.northeast.query(range_rect, found)
self.southwest.query(range_rect, found)
self.southeast.query(range_rect, found)
return found
# ---- Example usage ----
if __name__ == "__main__":
boundary = Rectangle(x=0, y=0, hw=50, hh=50)
qt = QuadTree(boundary, capacity=4)
import random
for _ in range(100):
pt = (random.uniform(-50, 50), random.uniform(-50, 50))
qt.insert(pt)
# Query a region
range_q = Rectangle(x=10, y=10, hw=20, hh=20)
pts_in_range = qt.query(range_q)
print(f"Found {len(pts_in_range)} points in query rectangle.")